Install Polkadot SDK¶
This guide provides step-by-step instructions for installing the Polkadot SDK on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The installation process consists of two main parts:
- Installing dependencies: Setting up Rust, required system packages, and development tools.
- Building the Polkadot SDK: Cloning and compiling the Polkadot SDK repository.
Follow the appropriate section for your operating system to ensure all necessary tools are installed and configured properly.
Install Dependencies: macOS¶
You can install Rust and set up a Substrate development environment on Apple macOS computers with Intel or Apple M1 processors.
Before You Begin¶
Before you install Rust and set up your development environment on macOS, verify that your computer meets the following basic requirements:
- Operating system version is 10.7 Lion or later.
- Processor speed of at least 2 GHz. Note that 3 GHz is recommended.
- Memory of at least 8 GB RAM. Note that 16 GB is recommended.
- Storage of at least 10 GB of available space.
- Broadband Internet connection.
Install Homebrew¶
In most cases, you should use Homebrew to install and manage packages on macOS computers. If you don't already have Homebrew installed on your local computer, you should download and install it before continuing.
To install Homebrew:
- Open the Terminal application.
-
Download and install Homebrew by running the following command:
-
Verify Homebrew has been successfully installed by running the following command:
The command displays output similar to the following:
brew --version Homebrew 4.3.15
Support for Apple Silicon¶
Protobuf must be installed before the build process can begin. To install it, run the following command:
Install Required Packages and Rust¶
Because the blockchain requires standard cryptography to support the generation of public/private key pairs and the validation of transaction signatures, you must also have a package that provides cryptography, such as openssl.
To install openssl and the Rust toolchain on macOS:
- Open the Terminal application.
-
Ensure you have an updated version of Homebrew by running the following command:
-
Install the
opensslpackage by running the following command: -
Download the
rustupinstallation program and use it to install Rust by running the following command: -
Follow the prompts displayed to proceed with a default installation.
-
Update your current shell to include Cargo by running the following command:
-
Configure the Rust toolchain to default to the latest stable version by running the following commands:
-
Install
cmakeusing the following command: -
Proceed to Build the Polkadot SDK.
Install Dependencies: Linux¶
Rust supports most Linux distributions. Depending on the specific distribution and version of the operating system you use, you might need to add some software dependencies to your environment. In general, your development environment should include a linker or a C-compatible compiler, such as clang, and an appropriate integrated development environment (IDE).
Before You Begin¶
Check the documentation for your operating system for information about the installed packages and how to download and install any additional packages you might need. For example, if you use Ubuntu, you can use the Ubuntu Advanced Packaging Tool (apt) to install the build-essential package:
At a minimum, you need the following packages before you install Rust:
Because the blockchain requires standard cryptography to support the generation of public/private key pairs and the validation of transaction signatures, you must also have a package that provides cryptography, such as libssl-dev or openssl-devel.
Install Required Packages and Rust¶
To install the Rust toolchain on Linux:
- Open a terminal shell.
- Check the packages installed on the local computer by running the appropriate package management command for your Linux distribution.
-
Add any package dependencies you are missing to your local development environment by running the appropriate package management command for your Linux distribution:
Remember that different distributions might use different package managers and bundle packages in different ways. For example, depending on your installation selections, Ubuntu Desktop and Ubuntu Server might have different packages and different requirements. However, the packages listed in the command-line examples are applicable to many common Linux distributions, including Debian, Linux Mint, MX Linux, and Elementary OS.
-
Download the
rustupinstallation program and use it to install Rust by running the following command: -
Follow the prompts displayed to proceed with a default installation.
-
Update your current shell to include Cargo by running the following command:
-
Verify your installation by running the following command:
-
Configure the Rust toolchain to default to the latest stable version by running the following commands:
-
Proceed to Build the Polkadot SDK.
Install Dependencies: Windows (WSL)¶
In general, UNIX-based operating systems—like macOS or Linux—provide a better development environment for building Substrate-based blockchains.
However, suppose your local computer uses Microsoft Windows instead of a UNIX-based operating system. In that case, you can configure it with additional software to make it a suitable development environment for building Substrate-based blockchains. To prepare a development environment on a Microsoft Windows computer, you can use Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) to emulate a UNIX operating environment.
Before You Begin¶
Before installing on Microsoft Windows, verify the following basic requirements:
- You have a computer running a supported Microsoft Windows operating system:
- For Windows desktop: You must be running Microsoft Windows 10, version 2004 or later, or Microsoft Windows 11 to install WSL.
- For Windows server: You must be running Microsoft Windows Server 2019, or later, to install WSL on a server operating system.
- You have a good internet connection and access to a shell terminal on your local computer.
Set Up Windows Subsystem for Linux¶
WSL enables you to emulate a Linux environment on a computer that uses the Windows operating system. The primary advantage of this approach for Substrate development is that you can use all of the code and command-line examples as described in the Substrate documentation. For example, you can run common commands—such as ls and ps—unmodified. By using WSL, you can avoid configuring a virtual machine image or a dual-boot operating system.
To prepare a development environment using WSL:
-
Check your Windows version and build number to see if WSL is enabled by default.
If you have Microsoft Windows 10, version 2004 (Build 19041 and higher), or Microsoft Windows 11, WSL is available by default and you can continue to the next step.
If you have an older version of Microsoft Windows installed, see the WSL manual installation steps for older versions. If you are installing on an older version of Microsoft Windows, you can download and install WLS 2 if your computer has Windows 10, version 1903 or higher.
-
Select Windows PowerShell or Command Prompt from the Start menu, right-click, then Run as administrator.
-
In the PowerShell or Command Prompt terminal, run the following command:
This command enables the required WSL 2 components that are part of the Windows operating system, downloads the latest Linux kernel, and installs the Ubuntu Linux distribution by default.
If you want to review the other Linux distributions available, run the following command:
-
After the distribution is downloaded, close the terminal.
-
Click the Start menu, select Shut down or sign out, then click Restart to restart the computer.
Restarting the computer is required to start the installation of the Linux distribution. It can take a few minutes for the installation to complete after you restart.
For more information about setting up WSL as a development environment, see the Set up a WSL development environment docs.
Install Required Packages and Rust¶
To install the Rust toolchain on WSL:
- Click the Start menu, then select Ubuntu.
- Type a UNIX user name to create a user account.
- Type a password for your UNIX user, then retype the password to confirm it.
-
Download the latest updates for the Ubuntu distribution using the Ubuntu Advanced Packaging Tool (
apt) by running the following command: -
Add the required packages for the Ubuntu distribution by running the following command:
-
Download the
rustupinstallation program and use it to install Rust for the Ubuntu distribution by running the following command: -
Follow the prompts displayed to proceed with a default installation.
-
Update your current shell to include Cargo by running the following command:
-
Verify your installation by running the following command:
-
Configure the Rust toolchain to use the latest stable version as the default toolchain by running the following commands:
-
Proceed to Build the Polkadot SDK.
Build the Polkadot SDK¶
After installing all dependencies, you can now clone and compile the Polkadot SDK repository to verify your setup.
Clone the Polkadot SDK¶
-
Clone the Polkadot SDK repository:
-
Navigate into the project directory:
Compile the Polkadot SDK¶
Compile the entire Polkadot SDK repository to ensure your environment is properly configured:
Note
This initial compilation will take significant time, depending on your machine specifications. It compiles all components of the Polkadot SDK to verify your toolchain is correctly configured.
Verify the Build¶
Once the build completes successfully, verify the installation by checking the compiled binaries:
You should see several binaries, including:
polkadot: The Polkadot relay chain node.polkadot-parachain: The parachain collator node.polkadot-omni-node:The omni node for running parachains.substrate-node: The kitchensink node with many pre-configured pallets.
Verify the Polkadot binary works by checking its version:
This should display version information similar to:
If you see the version output without errors, your development environment is correctly configured and ready for Polkadot SDK development!
Optional: Run the Kitchensink Node¶
The Polkadot SDK includes a feature-rich node called "kitchensink" located at substrate/bin/node. This node comes pre-configured with many pallets and features from the Polkadot SDK, making it an excellent reference for exploring capabilities and understanding how different components work together.
Note
If you've already compiled the Polkadot SDK in the previous step, the substrate-node binary is already built and ready to use. You can skip directly to running the node.
Run the Kitchensink Node in Development Mode¶
From the polkadot-sdk root directory, start the kitchensink node in development mode:
The --dev flag enables development mode, which:
- Runs a single-node development chain.
- Produces and finalizes blocks automatically.
- Uses pre-configured development accounts (Alice, Bob, etc.).
- Deletes all data when stopped, ensuring a clean state on restart.
You should see log output indicating the node is running and producing blocks, with increasing block numbers after finalized.
Interact with the Kitchensink Node¶
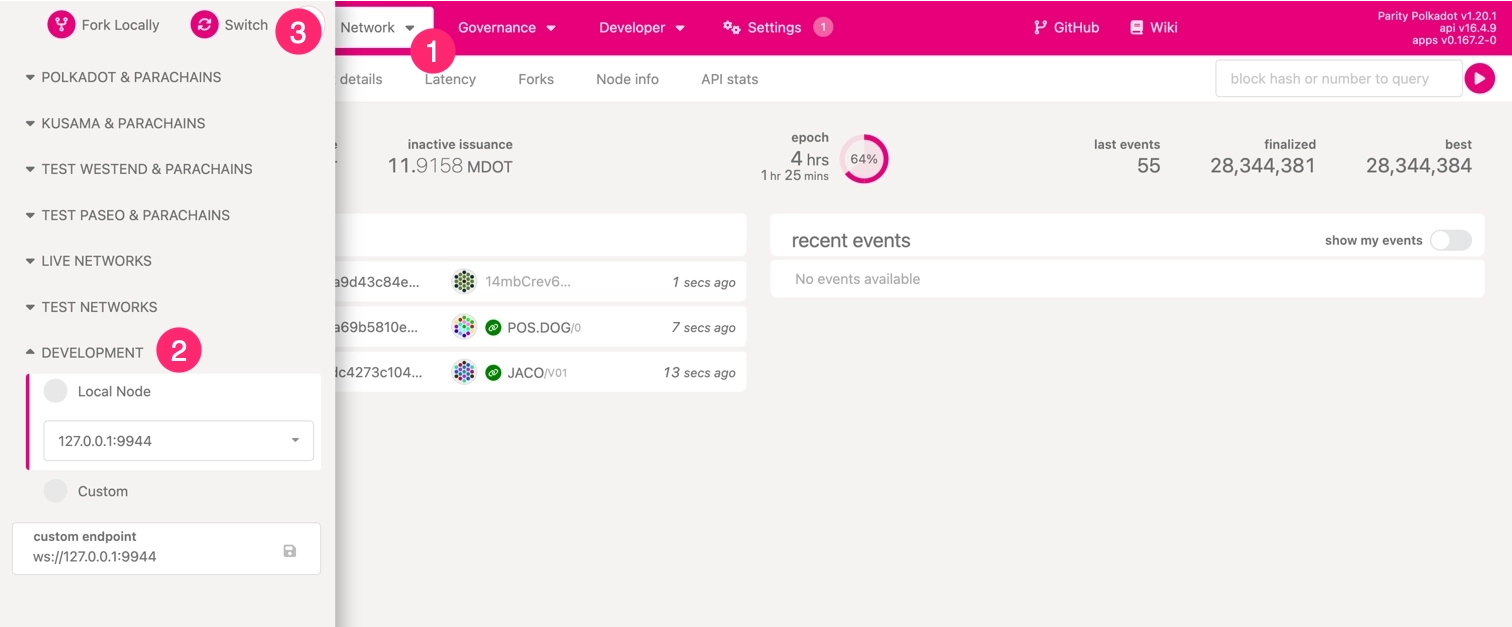
The kitchensink node is accessible at ws://localhost:9944. Open Polkadot.js Apps in your browser to explore its features and connect to the local node.
- Click the network icon in the top left corner.
- Scroll to Development and select Local Node.
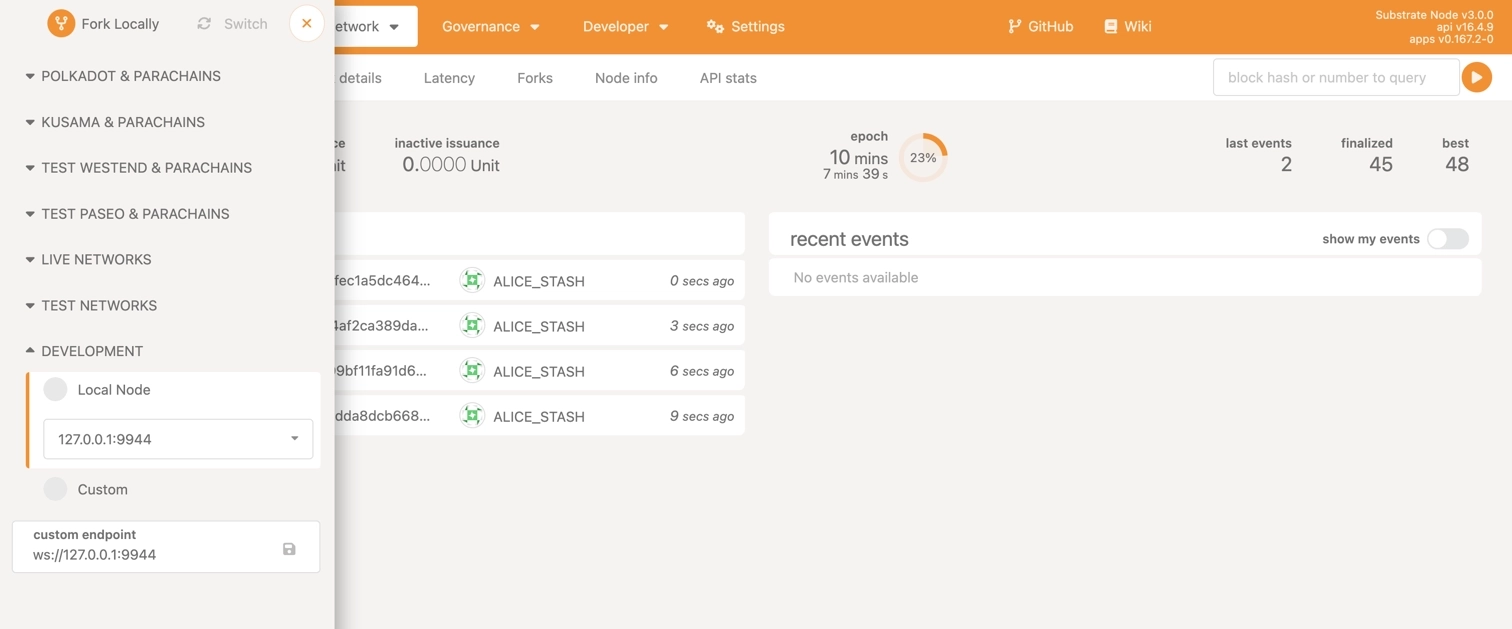
- Click Switch to connect to your local node.
Once connected, the interface updates its color scheme to indicate a successful connection to the local node.
You can now explore the various pallets and features included in the kitchensink node, making it a valuable reference as you develop your own blockchain applications.
To stop the node, press Control-C in the terminal.
Where to Go Next¶
-
Get Started with Parachain Development
Practical examples and tutorials for building and deploying Polkadot parachains, covering everything from launch to customization and cross-chain messaging.
| Created: October 18, 2024