Parachains Overview¶
Introduction¶
A parachain is a specialized blockchain that connects to the Polkadot relay chain, benefiting from shared security, interoperability, and scalability. Parachains are built using the Polkadot SDK, a powerful toolkit written in Rust that provides everything needed to create custom blockchain logic while integrating seamlessly with the Polkadot network.
Unlike standalone blockchains that must bootstrap their own validator sets and security, parachains leverage Polkadot's pooled security model. This allows parachain developers to focus on their application-specific functionality rather than consensus and security infrastructure. Parachains can communicate with each other through Cross-Consensus Messaging (XCM), enabling seamless interoperability across the Polkadot ecosystem.
Key capabilities that parachains provide include:
- Shared security: Inherit security from Polkadot's validator set without maintaining your own.
- Interoperability: Communicate trustlessly with other parachains via XCM.
- Scalability: Process transactions in parallel with other parachains.
- Customization: Build application-specific logic tailored to your use case.
- Upgradeability: Upgrade runtime logic without hard forks.
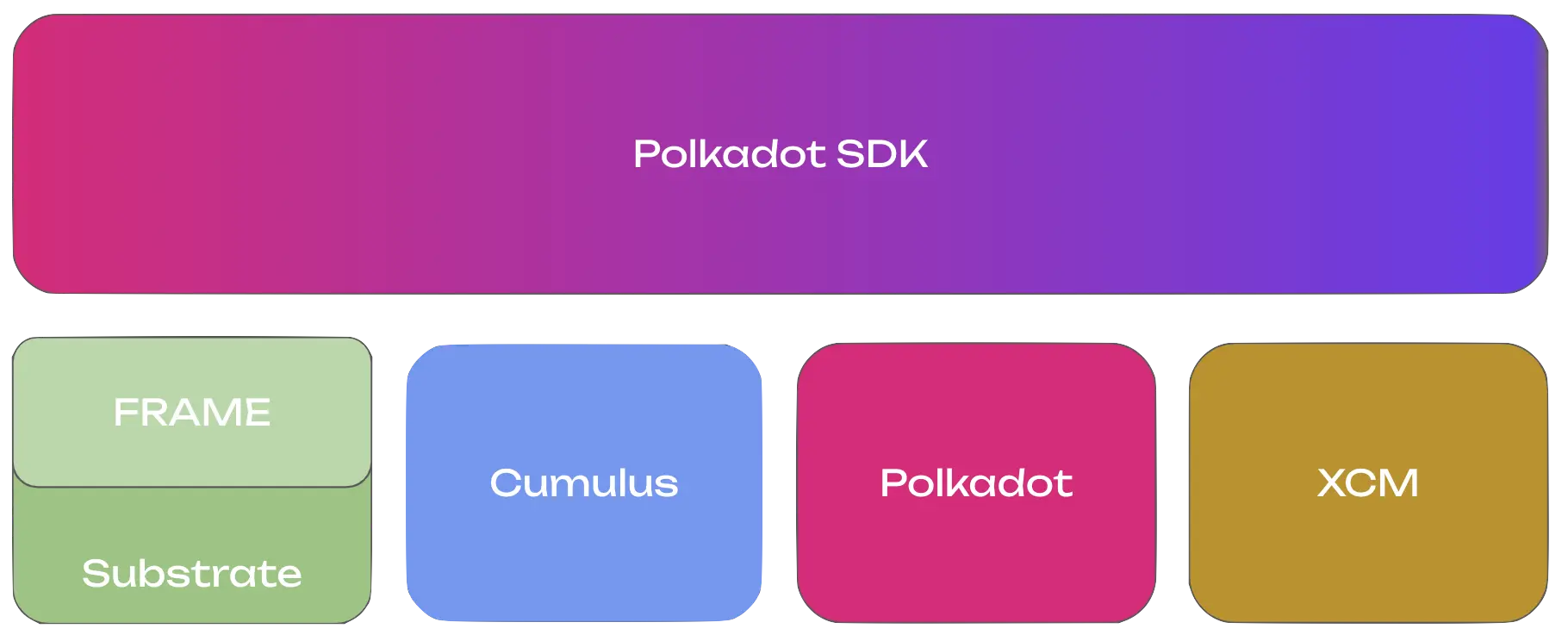
Polkadot SDK: Parachain Architecture¶
Building a parachain involves understanding and utilizing several key components of the Polkadot SDK:
- Substrate: The foundation providing core blockchain primitives and libraries.
- FRAME: A modular framework for building your parachain's runtime logic.
- Cumulus: Essential libraries and pallets that enable parachain functionality.
- XCM (Cross Consensus Messaging): The messaging format for communicating with other parachains and the relay chain.
- Polkadot: The relay chain that provides security and coordination.
Substrate: The Foundation¶
Substrate provides the core infrastructure that every parachain is built upon. It handles the low-level blockchain functionality, allowing you to focus on your application's unique features. Substrate includes implementations for networking, database management, consensus participation, and the execution environment for your runtime.
Every Polkadot SDK node consists of two main components:
-
Client (Host): Handles infrastructure services.
- Native binary that runs on validator and collator nodes.
- Executes the Wasm-compiled runtime.
- Manages networking, database, mempool, and block production.
- Interfaces with the relay chain for validation.
-
Runtime (State Transition Function): Contains your business logic.
- Defines how your Polkadot SDK node processes transactions.
- Compiled to Wasm for deterministic execution.
- Stored on-chain and upgradeable via governance.
%%{init: {'flowchart': {'padding': 5, 'nodeSpacing': 50, 'rankSpacing': 10}}}%%
graph TB
classDef title font-size:20px,font-weight:bold,stroke-width:0px
classDef clientStyle font-size:16px,font-weight:bold
classDef clientSubNodeStyle margin-top:10px
classDef runtimeCallExecutorStyle padding-top:10px
subgraph sg1[Parachain<br /> Node]
direction TB
I[RuntimeCall Executor]
B[Wasm Runtime - STF]
subgraph sg2[Client]
direction TB
C[Network and Blockchain<br/>Infrastructure Services<br/>+ Relay Chain Interface]
end
I --> B
end
class sg1 title
class sg2 clientStyle
class C clientSubNodeStyle
class I runtimeCallExecutorStyle
FRAME: Building Blocks for Your Runtime¶
FRAME provides modular components called pallets that you can compose to build your parachain's runtime. Each pallet provides specific functionality that you can customize and configure for your needs. This modular approach allows you to quickly assemble complex functionality without writing everything from scratch.
graph LR
subgraph SP["<b style='font-size:18px;'>Parachain Runtime</b>"]
direction LR
Timestamp ~~~ Aura ~~~ ParachainSystem
Balances ~~~ TransactionPayment ~~~ Sudo
subgraph Timestamp["Timestamp"]
SS1[Custom Config]
end
subgraph Aura["Aura"]
SS2[Custom Config]
end
subgraph ParachainSystem["Parachain System"]
SS3[Custom Config]
end
subgraph Balances["Balances"]
SS4[Custom Config]
end
subgraph TransactionPayment["Transaction Payment"]
SS5[Custom Config]
end
subgraph Sudo["Sudo"]
SS6[Custom Config]
end
style Timestamp stroke:#FF69B4
style Aura stroke:#FF69B4
style ParachainSystem stroke:#FF69B4
style Balances stroke:#FF69B4
style TransactionPayment stroke:#FF69B4
style Sudo stroke:#FF69B4
style SS1 stroke-dasharray: 5
style SS2 stroke-dasharray: 5
style SS3 stroke-dasharray: 5
style SS4 stroke-dasharray: 5
style SS5 stroke-dasharray: 5
style SS6 stroke-dasharray: 5
end
subgraph AP["<b style='font-size:18px;'>Available FRAME Pallets</b>"]
direction LR
A1[Aura]~~~A2[Parachain<br>System]~~~A3[Transaction<br>Payment]~~~A4[Sudo]
B1[Identity]~~~B2[Balances]~~~B3[Assets]~~~B4[EVM]
C1[Timestamp]~~~C2[Staking]~~~C3[Contracts]~~~C4[and more...]
end
AP --> SPCumulus: Parachain-Specific Functionality¶
Cumulus is what transforms a Polkadot SDK-based runtime into a parachain-capable runtime. It provides the essential components for communicating with the relay chain, participating in Polkadot's consensus, and handling parachain-specific operations like block validation and collation.
Key Cumulus components include:
- Parachain system pallet: Core parachain functionality and relay chain communication.
- Collator consensus: Block production logic for parachain collators.
- Relay chain interface: APIs for interacting with the Polkadot relay chain.
- Validation data: Handling proof-of-validity data required by relay chain validators.
Where to Go Next¶
Building a parachain requires understanding the relationship between your chain and the Polkadot relay chain. The Polkadot SDK provides all the tools needed to design custom runtime logic, enable cross-chain communication, and deploy your parachain to production.
The following sections provide detailed guidance on each aspect of parachain development, from initial design through deployment and ongoing maintenance.
-
Guide Launch a Simple Parachain
Walk through the complete parachain launch flow: from setup and deployment to obtaining coretime.
-
Guide Customize Your Runtime
Design your parachain's runtime logic and choose appropriate pallets for your use case.
-
Guide Interoperability
Implement XCM for trustless cross-chain communication with other parachains.
-
Guide Runtime Upgrades
Upgrade your parachain's runtime without hard forks using forkless upgrade mechanisms.
| Created: January 14, 2026