System Precompile¶
Introduction¶
The System precompile provides access to essential runtime-level functionality that smart contracts frequently need. Located at the fixed address 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000900, it offers a comprehensive set of utilities, including:
- Cryptographic operations: BLAKE2 hashing, sr25519 signature verification, and ECDSA operations.
- Account management: Account ID conversions and balance queries.
- Runtime queries: Origin checks, code hash retrieval, and weight tracking.
- Contract lifecycle: Safe contract termination.
This precompile is particularly useful for contracts that need to interact with Polkadot-native cryptographic primitives or query runtime state information.
Precompile Interface¶
The System precompile implements the ISystem interface, which is defined in the Polkadot SDK. The source code for the interface is as follows:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
address constant SYSTEM_ADDR = 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000900;
interface ISystem {
/// Computes the BLAKE2 256-bit hash on the given input.
function hashBlake256(bytes memory input) external pure returns (bytes32 digest);
/// Computes the BLAKE2 128-bit hash on the given input.
function hashBlake128(bytes memory input) external pure returns (bytes32 digest);
/// Retrieve the account id for a specified `H160` address.
///
/// Calling this function on a native `H160` chain (`type AccountId = H160`)
/// does not make sense, as it would just return the `address` that it was
/// called with.
///
/// # Note
///
/// If no mapping exists for `addr`, the fallback account id will be returned.
function toAccountId(address input) external view returns (bytes memory account_id);
/// Checks whether the caller of the contract calling this function is the origin
/// of the whole call stack.
function callerIsOrigin() external view returns (bool);
/// Checks whether the caller of the contract calling this function is root.
///
/// Note that only the origin of the call stack can be root. Hence this
/// function returning `true` implies that the contract is being called by the origin.
///
/// A return value of `true` indicates that this contract is being called by a root origin,
/// and `false` indicates that the caller is a signed origin.
function callerIsRoot() external view returns (bool);
/// Returns the minimum balance that is required for creating an account
/// (the existential deposit).
function minimumBalance() external view returns (uint);
/// Returns the code hash of the caller.
function ownCodeHash() external view returns (bytes32);
/// Returns the amount of `Weight` left.
function weightLeft() external view returns (uint64 refTime, uint64 proofSize);
/// Terminate the calling contract of this function and send balance to `beneficiary`.
/// This will revert if:
/// - called from constructor
/// - called from static context
/// - called from delegate context
/// - the contract introduced balance locks
function terminate(address beneficiary) external;
/// Verify a sr25519 signature
///
/// # Parameters
///
/// - `signature`: The signature bytes.
/// - `message`: The message bytes.
/// - `publicKey`: The public key bytes.
function sr25519Verify(uint8[64] calldata signature, bytes calldata message, bytes32 publicKey) external view returns (bool);
/// Calculates the Ethereum address from the ECDSA compressed public key.
/// This fails if ECDSA recovery of the provided key fails.
///
/// # Parameters
///
/// - `publicKey`: The public key bytes.
function ecdsaToEthAddress(uint8[33] calldata publicKey) external view returns (bytes20);
}
For the complete implementation, refer to the ISystem.sol file in the Polkadot SDK.
Cryptographic Operations¶
Compute BLAKE2-256 Hash¶
Computes the BLAKE2 256-bit hash of the provided input data. BLAKE2 is the native hashing algorithm used throughout the Polkadot ecosystem and is more efficient than SHA-256 for most operations.
Parameters:
input: The data to hash.
Returns:
digest: The 32-byte BLAKE2-256 hash.
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
bytes memory data = "Hello Polkadot!";
bytes32 hash = system.hashBlake256(data);
Compute BLAKE2-128 Hash¶
Computes the BLAKE2 128-bit hash of the provided input data. This variant is useful when a shorter hash is acceptable for your use case.
Parameters:
input: The data to hash.
Returns:
digest: The 16-byte BLAKE2-128 hash (returned as bytes32 with padding).
Verify SR25519 Signature¶
Verifies a sr25519 signature. Sr25519 is the signature scheme used by most accounts on Polkadot and is essential for verifying signatures from Polkadot native wallets.
function sr25519Verify(uint8[64] calldata signature, bytes calldata message, bytes32 publicKey) external view returns (bool);
Parameters:
signature: The 64-byte signature to verify.message: The message that was signed.publicKey: The 32-byte public key.
Returns:
bool:trueif the signature is valid,falseotherwise.
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
uint8[64] memory sig = ...; // The signature bytes
bytes memory message = "Sign this message";
bytes32 pubKey = 0x...; // The sr25519 public key
bool isValid = system.sr25519Verify(sig, message, pubKey);
require(isValid, "Invalid signature");
Convert ECDSA Public Key to Ethereum Address¶
Converts a compressed ECDSA public key to an Ethereum address. This is useful when working with Ethereum-style accounts, and you need to derive addresses from public keys.
Parameters:
publicKey: The 33-byte compressed ECDSA public key.
Returns:
bytes20: The derived Ethereum address.
Account Management¶
Convert Address to Account ID¶
Converts an H160 Ethereum-style address to the native account ID format used by the runtime. This is crucial when contracts need to interact with runtime functionality that expects account IDs rather than addresses.
Parameters:
input: The Ethereum address to convert.
Returns:
account_id: The native account ID bytes.
Note
If no mapping exists for the provided address, a fallback account ID will be returned.
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
address ethAddr = 0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890;
bytes memory accountId = system.toAccountId(ethAddr);
Runtime Queries¶
Check if Caller is Origin¶
Checks whether the immediate caller of your contract is the origin (the initial caller) of the entire call stack. This is useful for determining if your contract was called directly by a user or through another contract.
Returns:
bool:trueif the caller is the origin,falseif called through another contract.
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
require(system.callerIsOrigin(), "Must be called directly by user");
Check if Caller is Root¶
Checks whether the caller is a root origin. Root origins have elevated privileges and can perform privileged operations. Note that if this returns true, callerIsOrigin() will also return true, as only the origin can be root.
Returns:
bool:trueif the caller is root,falseotherwise.
Get Minimum Balance¶
Returns the existential deposit - the minimum balance required for an account to exist on the chain. Accounts with balances below this threshold are reaped (removed) from state.
Returns:
uint: The minimum balance in the smallest unit of the native token.
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
uint minBalance = system.minimumBalance();
require(msg.value >= minBalance, "Below existential deposit");
Get Own Code Hash¶
Returns the code hash of the calling contract. This can be used for contract identity verification or to check if a contract has been upgraded.
Returns:
bytes32: The BLAKE2-256 hash of the contract's code.
Get Weight Left¶
Returns the amount of computational resources (weight) remaining in the current execution context. Weight is Polkadot's measure of computational cost, consisting of two components:
Returns:
refTime: Remaining reference time (computational cycles).proofSize: Remaining proof size allowance (storage proof bytes).
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
(uint64 refTime, uint64 proofSize) = system.weightLeft();
require(refTime > 1000000, "Insufficient weight remaining");
Contract Lifecycle¶
Terminate Contract¶
Terminates the calling contract and transfers its remaining balance to a specified beneficiary. This is useful for cleanup or when a contract has fulfilled its purpose.
Parameters:
beneficiary: The address that will receive the contract's remaining balance.
Warning
This function will revert if called from:
- A constructor
- A static context
- A delegate context
- A contract with balance locks
Example usage:
ISystem system = ISystem(SYSTEM_ADDR);
address beneficiary = 0x1234567890123456789012345678901234567890;
system.terminate(beneficiary); // Contract is terminated after this call
Interact with the System Precompile¶
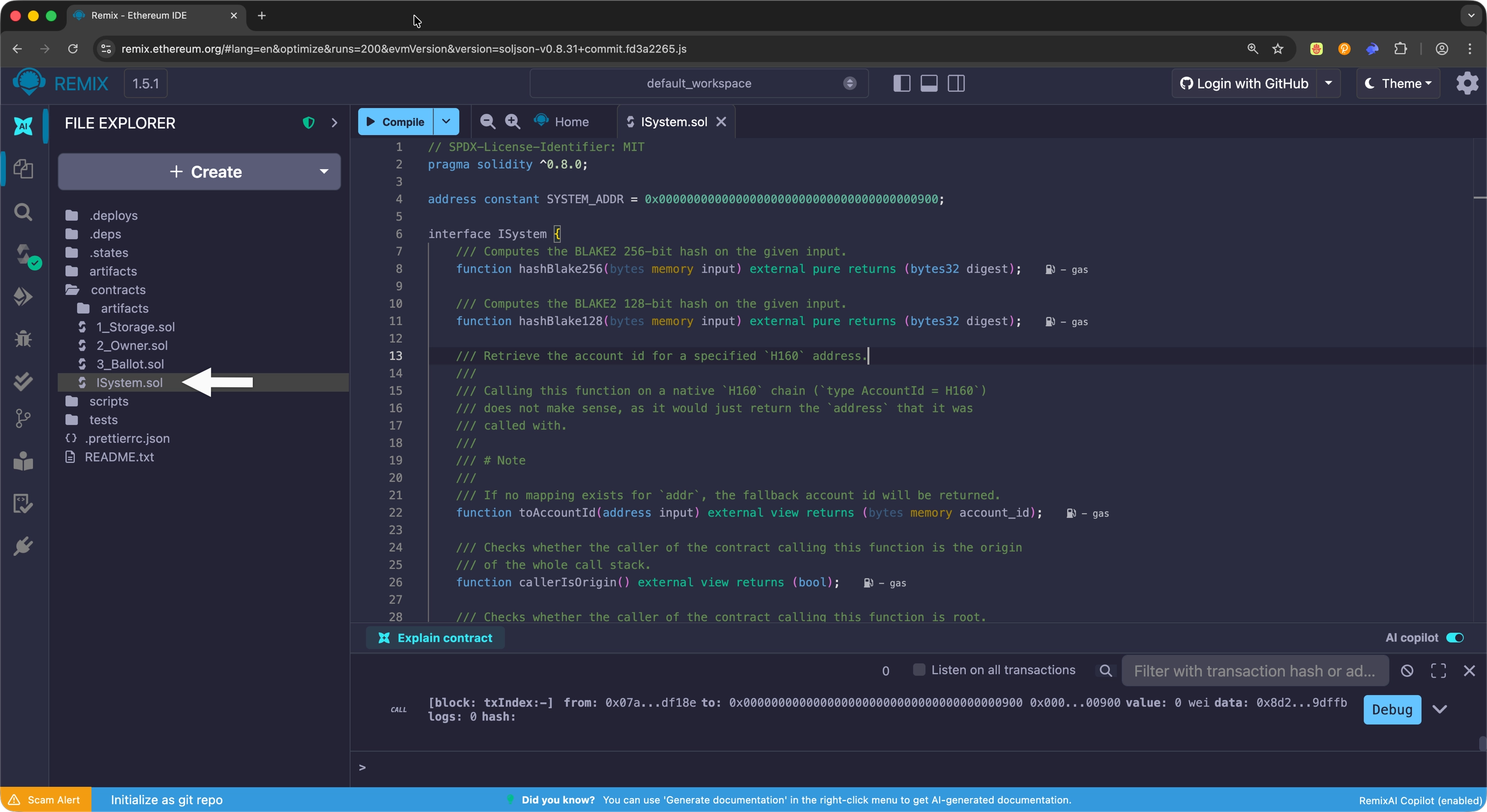
To interact with the System precompile in the Remix IDE:
- Create a new file called
ISystem.solin Remix. -
Copy and paste the
ISysteminterface code into the file. -
Compile the interface using the Compile button at the top or press Ctrl + S.
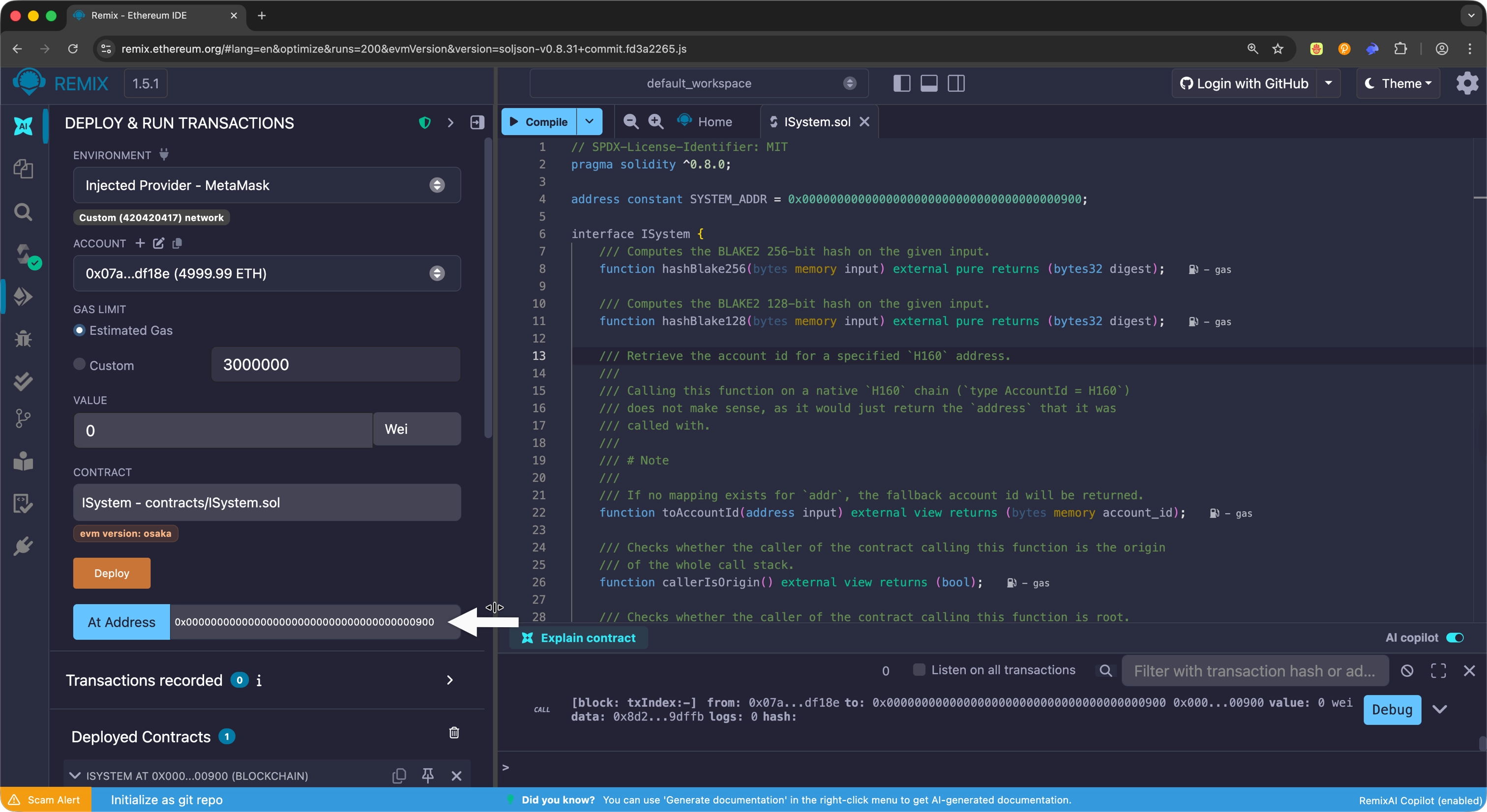
- In the Deploy & Run Transactions tab, select the
ISysteminterface from the contract dropdown. - Enter the precompile address
0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000900in the At Address input field. -
Select the At Address button to connect to the precompile.
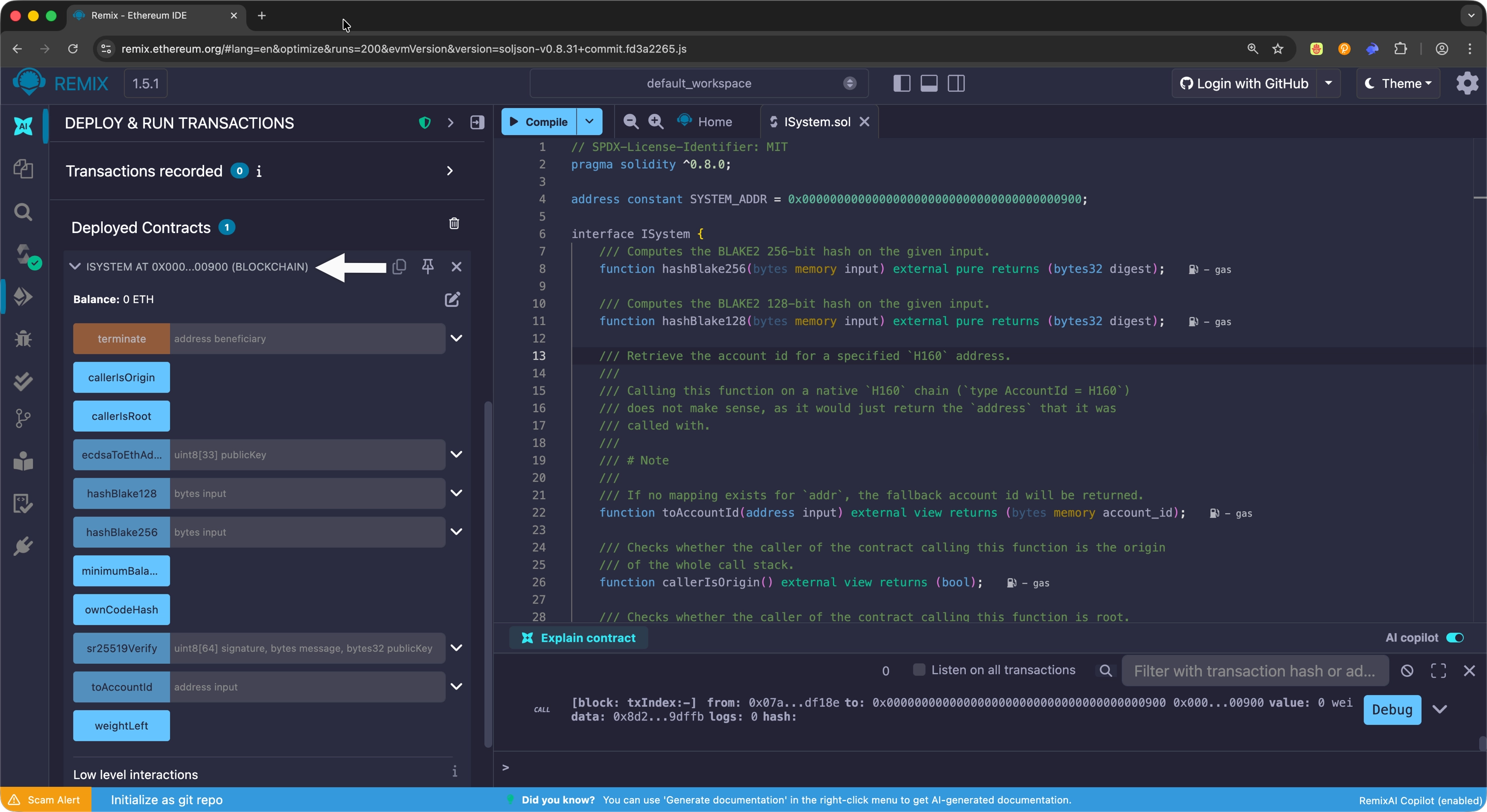
Once connected, you can interact with any of the System precompile functions directly through the Remix interface.
Conclusion¶
The System precompile provides essential building blocks for smart contracts that need to interact with Polkadot-native functionality. By offering access to cryptographic primitives, runtime queries, and system utilities, it enables developers to build sophisticated applications that leverage the full power of the Polkadot runtime.
Whether you're building identity systems that verify sr25519 signatures, contracts that need precise weight management, or applications that interact with Polkadot's native account system, the System precompile offers the necessary tools to bridge the gap between smart contract logic and runtime functionality.
Reference¶
| Created: January 27, 2026